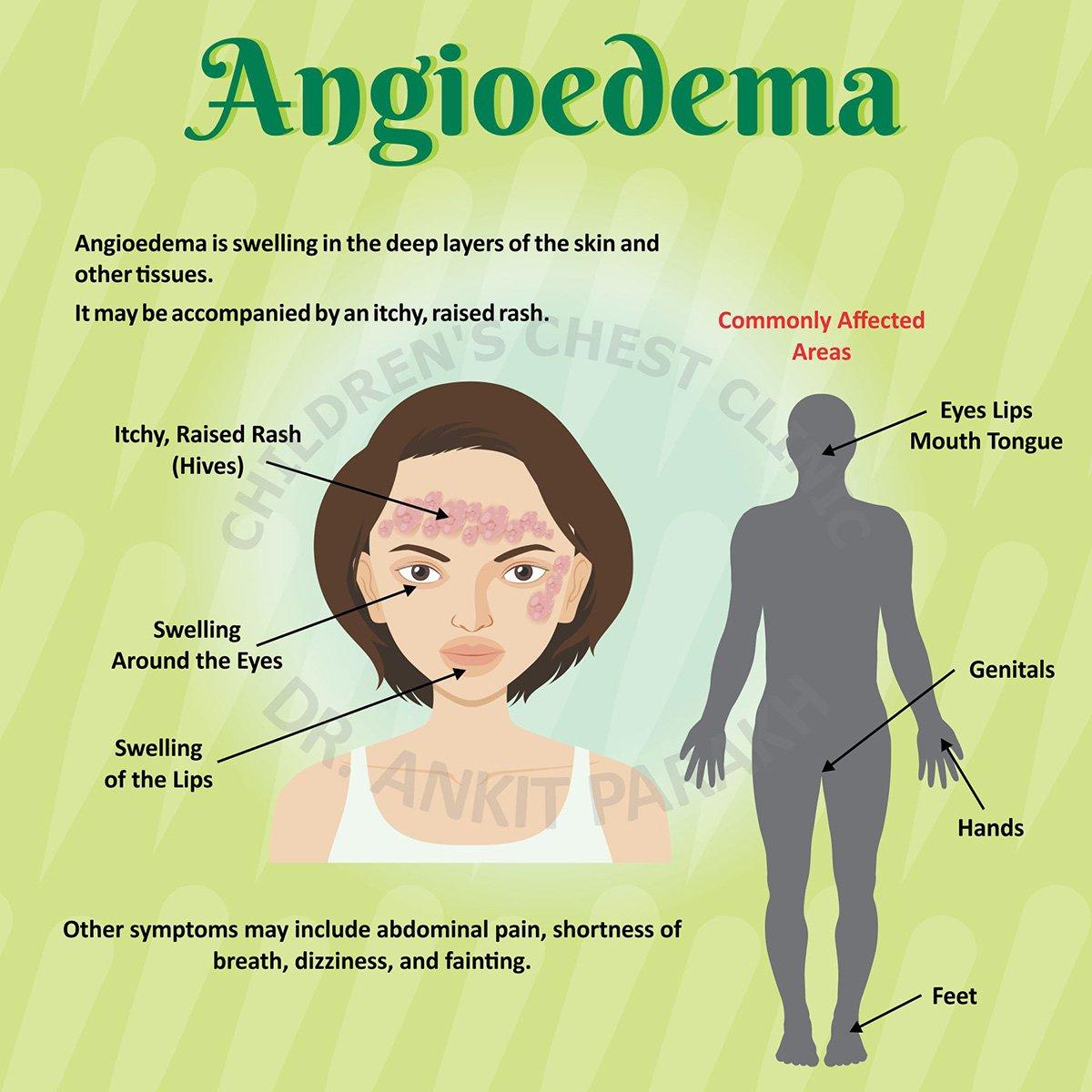
Angioedema is a medical condition characterized by rapid swelling of the deeper layers of the skin, often affecting areas like the face, lips, tongue, throat, or extremities. It can be a distressing and potentially life-threatening condition, especially when it involves the airways. Understanding the different types of angioedema, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is critical for effective management. This article explores the various forms of angioedema, their triggers, and how they can be addressed, including the role of medications like ceftriaxone injection wholesaler in specific cases.
What is Angioedema?
Angioedema involves swelling beneath the skin’s surface, typically caused by the leakage of fluid from blood vessels into surrounding tissues. Unlike hives (urticaria), which affect the superficial layers of the skin, angioedema occurs in deeper tissues, leading to more pronounced and potentially dangerous swelling. It can occur alone or in conjunction with hives. The condition may be acute (lasting a few hours to days) or chronic (recurring over weeks or months).
Angioedema is often linked to an immune response or vascular changes triggered by various factors, such as allergies, medications, infections, or genetic predispositions. Treatment often involves addressing the underlying cause and may include medications supplied by a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler when infections are a contributing factor.
Types of Angioedema
Angioedema is classified into several types based on its cause and underlying mechanism. Below are the primary types:
1. Allergic Angioedema
Allergic angioedema is the most common form and is typically triggered by an allergic reaction to substances such as foods (e.g., nuts, shellfish, eggs), medications (e.g., penicillin, aspirin), insect stings, or environmental allergens like pollen. The immune system releases histamine and other chemicals, causing blood vessels to leak fluid into surrounding tissues.
-
Symptoms: Swelling of the lips, eyes, tongue, or throat; hives; itching; and, in severe cases, difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis.
-
Triggers: Common allergens include foods, drugs, and insect bites.
-
Treatment: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine (in severe cases) are used to manage symptoms. If an infection is suspected as a trigger, antibiotics from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler may be prescribed to address the underlying infection.
2. Drug-Induced Angioedema
Certain medications, particularly angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors used for hypertension, can cause angioedema. This type is not always allergic in nature and may occur months or years after starting the medication. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antibiotics can also trigger this form.
-
Symptoms: Swelling in the face, lips, or tongue, often without hives. Airway involvement can be life-threatening.
-
Triggers: ACE inhibitors (e.g., lisinopril), NSAIDs, or certain antibiotics.
-
Treatment: Discontinuing the offending drug is critical. Supportive care, including antihistamines or corticosteroids, may be used. In cases where an infection-related trigger is identified, sourcing antibiotics from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler can help manage complications.
3. Hereditary Angioedema (HAE)
Hereditary angioedema is a rare genetic disorder caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of C1 inhibitor, a protein that regulates the complement system and prevents excessive inflammation. HAE is not associated with hives and can occur spontaneously or be triggered by stress, trauma, or infections.
-
Symptoms: Recurrent swelling in the extremities, face, genitals, or gastrointestinal tract; abdominal pain; and potential airway obstruction.
-
Triggers: Stress, minor trauma, hormonal changes, or infections.
-
Treatment: C1 inhibitor replacement therapy, bradykinin receptor antagonists, or kallikrein inhibitors are used. If an infection exacerbates HAE, antibiotics from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler may be required to treat the underlying cause.
4. Acquired Angioedema
Acquired angioedema is similar to HAE but occurs later in life and is not genetic. It is often associated with autoimmune disorders, malignancies (e.g., lymphoma), or infections that deplete C1 inhibitor levels.
-
Symptoms: Similar to HAE, with swelling in deeper tissues, often without hives.
-
Triggers: Underlying conditions like autoimmune diseases or infections.
-
Treatment: Addressing the underlying condition is key. Immunosuppressants or chemotherapy may be needed for malignancies. Antibiotics from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler can help manage infections that trigger symptoms.
5. Idiopathic Angioedema
When no clear cause can be identified, angioedema is classified as idiopathic. This type is often chronic and may be associated with underlying immune dysregulation or undiagnosed triggers.
-
Symptoms: Recurrent swelling without an identifiable trigger, sometimes accompanied by hives.
-
Triggers: Unknown, though stress or minor infections may contribute.
-
Treatment: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressive therapy may be tried. If infections are suspected, antibiotics from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler may be used to rule out infectious triggers.
6. Vibratory Angioedema
This rare form is triggered by physical stimuli, such as vibration (e.g., using a lawnmower or power tools). It is considered a physical urticaria variant but can involve deeper tissue swelling.
-
Symptoms: Localized swelling and redness after exposure to vibration.
-
Triggers: Vibratory stimuli.
-
Treatment: Avoiding triggers and using antihistamines. Infections are rarely involved, but if present, a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler may supply antibiotics for treatment.
Diagnosis of Angioedema
Diagnosing angioedema involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes laboratory tests. Key diagnostic steps include:
-
History and Triggers: Identifying potential allergens, medications, or family history of swelling.
-
Blood Tests: Measuring C1 inhibitor levels, complement proteins (C4), or autoantibodies for HAE or acquired angioedema.
-
Allergy Testing: Skin or blood tests to identify allergic triggers.
-
Imaging or Biopsies: Used in acquired angioedema to rule out malignancies or other underlying conditions.
In cases where infections are suspected, such as in HAE or acquired angioedema exacerbations, antibiotics sourced from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler may be part of the diagnostic and treatment process to address bacterial causes.
Treatment and Management
Treatment varies depending on the type and severity of angioedema:
-
Allergic Angioedema: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine for severe cases. Avoiding allergens is crucial.
-
Drug-Induced: Discontinuing the offending drug and managing symptoms with antihistamines or corticosteroids.
-
Hereditary and Acquired Angioedema: C1 inhibitor replacement, bradykinin inhibitors, or supportive care. Treating underlying infections with antibiotics from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler can prevent exacerbations.
-
Idiopathic: Trial of antihistamines, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressive therapies.
-
Vibratory: Avoidance of triggers and symptomatic relief with antihistamines.
In emergencies, airway management is critical. Intubation or tracheostomy may be needed if swelling obstructs breathing.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Preventing angioedema involves identifying and avoiding triggers. For allergic angioedema, this means avoiding known allergens. For drug-induced cases, alternative medications should be used. HAE patients may benefit from prophylactic therapies to reduce attack frequency. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers and access to medications, including antibiotics from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler for infection-related triggers, are essential for managing chronic or recurrent cases.
Conclusion
Angioedema is a complex condition with multiple types, each requiring specific diagnostic and treatment approaches. From allergic reactions to genetic disorders, understanding the underlying cause is key to effective management. Medications, including those sourced from a ceftriaxone injection wholesaler, play a critical role in treating infections that may exacerbate angioedema. By recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate care, individuals can manage this condition effectively and reduce the risk of life-threatening complications.