Introduction: The Foundation of Modern Microscopy in Life Sciences
The biological microscope has long served as a cornerstone of scientific research and education in biology and medical sciences. Designed specifically to magnify and observe specimens such as cells, tissues, and microorganisms, biological microscopes allow scientists and students to explore the micro-world with extraordinary detail.
Whether used in academic labs, hospitals, or research institutions, these microscopes have enabled fundamental discoveries in cellular biology, microbiology, pathology, and genetics. With continued innovation, today’s biological microscopes are more powerful, precise, and user-friendly than ever before, making them essential instruments in scientific progress. Biological microscope market is projected to grow to USD 3.9 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.15% during 2024-2032.
Understanding the Biological Microscope: Components and Functionality
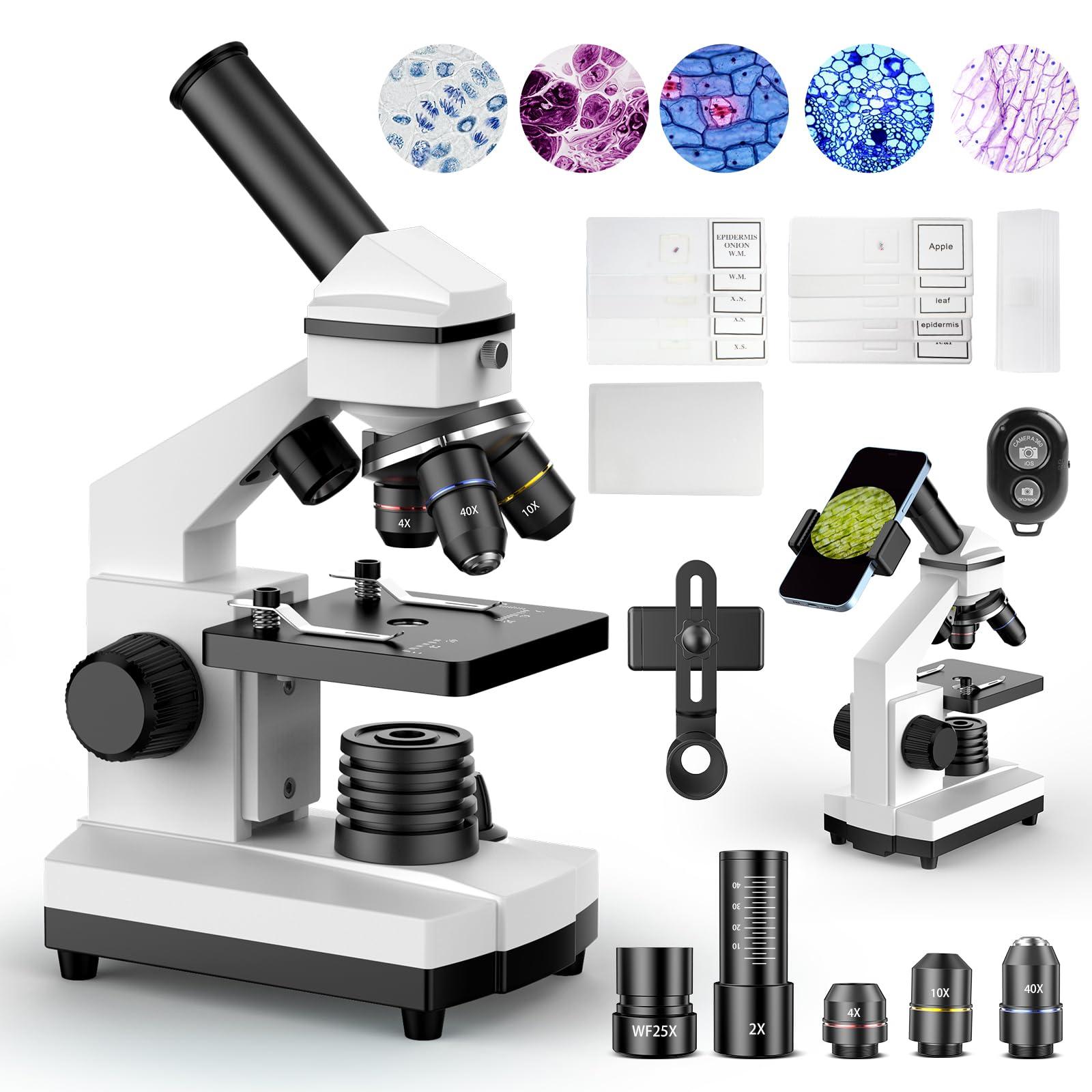
A biological microscope, also known as a compound light microscope, typically uses visible light and a series of lenses to magnify samples placed on glass slides. The microscope is composed of several critical components: the eyepiece (ocular lens), objective lenses, stage, light source, condenser, and focusing knobs.
The combination of objective and ocular lenses allows for magnifications typically ranging from 40x to 1000x. The condenser focuses light onto the specimen, while the diaphragm adjusts light intensity for contrast. Fine and coarse focusing knobs help achieve clear resolution, making even the smallest organelles visible. Some models also include digital imaging systems and software integration to capture and analyze images in real-time.
Types of Biological Microscopes: From Simple to Specialized Instruments
Biological microscopes are available in a range of models suited to different levels of application and expertise. Entry-level microscopes are commonly used in schools and colleges for educational purposes. These models usually have monocular or binocular eyepieces and basic light control features.
More advanced microscopes used in clinical laboratories or research centers often include trinocular heads for camera attachment, phase contrast capabilities, and fluorescence options. Inverted biological microscopes are designed to observe specimens in petri dishes or culture flasks, often used in cell culture and live cell imaging. Specialized models also support differential interference contrast (DIC) and confocal microscopy, which enhance imaging depth and clarity for high-end biological research.
Applications Across Fields: How Biological Microscopes Drive Research and Diagnosis
The utility of biological microscopes spans a wide range of fields. In medicine, they are critical in pathology labs for examining blood smears, tissue biopsies, and identifying infectious agents. In microbiology, microscopes help scientists study bacteria, viruses, and fungi, facilitating the development of vaccines and antibiotics.
Genetics and molecular biology use microscopes to study chromosomes and stained DNA samples, assisting in gene mapping and mutation detection. In environmental science, they help in analyzing soil microbes, algae, and water contaminants. Educational institutions rely on them to teach students about cell structures and biological processes, laying the foundation for careers in healthcare and science.
Key Market Players: Innovators in Biological Microscope Technology
Several manufacturers have established themselves as leaders in the biological microscope market by producing reliable and innovative models. Olympus Corporation, Nikon Instruments, Leica Microsystems, Zeiss Group, and Meiji Techno are some of the top players offering advanced biological microscopes.
These companies consistently integrate new technologies such as LED illumination, high-definition cameras, ergonomic designs, and image analysis software to enhance user experience. In the digital age, companies are also developing cloud-connected systems that allow researchers to share microscope images and collaborate remotely, an especially useful feature in academic and telemedicine settings.
Market Dynamics: Factors Driving the Demand for Biological Microscopes
The demand for biological microscopes continues to grow, driven by various market dynamics. One major factor is the rising investment in healthcare infrastructure and diagnostics, particularly in emerging economies. As more hospitals and laboratories are established, the need for diagnostic tools like microscopes increases.
Additionally, increased government and private funding in life sciences research boosts demand from academic and research institutions. Technological advancements, such as integration with AI-based image recognition, have also expanded the functional value of microscopes, making them indispensable in automated analysis. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on STEM education at the school and university level is creating steady demand for basic and mid-level microscope models.
Recent Developments: Innovation and Digitization Transforming the Industry
The biological microscope industry has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, primarily driven by digitization. Modern biological microscopes are increasingly equipped with high-resolution digital cameras, allowing for real-time image capture and live streaming of observations. Some models include touchscreen displays and built-in image analysis software, enabling immediate quantification of cell sizes, counts, and morphological data.
Another major trend is the miniaturization and portability of biological microscopes, which is particularly useful in field research and mobile medical units. Manufacturers are also working on enhancing user ergonomics, offering modular designs and adjustable viewing angles to reduce eye strain and fatigue during extended usage. Smart microscopes powered by machine learning algorithms are entering the market, offering automated sample recognition and classification, streamlining repetitive diagnostic tasks in clinical settings.
Regional Adoption: Biological Microscope Usage Across Global Markets
The adoption of biological microscopes varies across different regions based on education, healthcare infrastructure, and research activity. North America holds a significant share of the global market due to strong R&D investments, a well-established healthcare system, and robust academic networks. Europe follows closely, with countries like Germany, the UK, and France being major consumers of high-end biological microscopes for clinical and research purposes.
The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing rapid growth, particularly in China, India, and Japan, where increasing government investment in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and medical education is boosting microscope demand. Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are emerging markets, where improvements in healthcare access and educational facilities are gradually expanding the microscope user base.