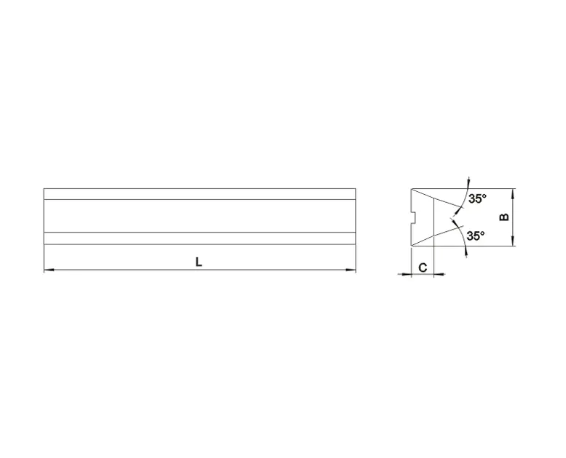
Carbide knives are becoming an essential tool in modern manufacturing due to their superior durability and precision. These knives, made from a composite material known for its hardness and resistance to wear, are commonly used in various industries, such as woodworking, metalworking, and plastic cutting. Unlike traditional steel knives, carbide blades provide exceptional longevity, allowing for fewer replacements and reduced downtime in production lines.
One of the primary benefits of carbide knives is their ability to maintain sharpness for extended periods. In high-volume manufacturing settings, where precision and efficiency are crucial, carbide knives can handle the demands of continuous cutting without compromising performance. The material’s toughness makes it ideal for tasks that require intricate cuts or the handling of hard materials, which would quickly dull a steel blade.
Additionally, carbide knives contribute to more accurate cuts. The material’s rigidity ensures that the knives do not flex or bend under pressure, resulting in cleaner, more precise edges. This is especially important in applications like the automotive or aerospace industries, where the quality of components depends on exact dimensions. Carbide knives are also highly resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in harsh environments where moisture or chemicals are present.
In terms of cost-effectiveness, while carbide knives may have a higher initial purchase price compared to their steel counterparts, their extended lifespan and consistent performance can offset this investment over time. Businesses that prioritize efficiency and quality can benefit greatly from using carbide knives in their operations.
In conclusion, carbide knives offer a combination of durability, precision, and cost-effectiveness that makes them an indispensable tool in various manufacturing processes. Their resistance to wear and ability to maintain sharpness over time ensure that companies can achieve high-quality results with reduced maintenance and downtime.